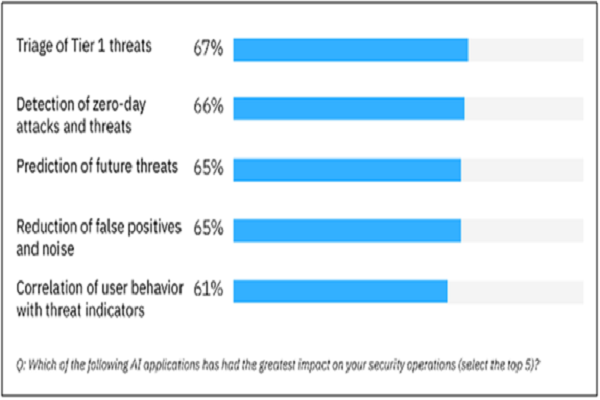
Only 7% of the companies are not considering using AI for cybersecurity. Leading organizations that have successfully integrated AI technology into their cybersecurity operations demonstrate the remarkable potential of AI in enhancing defense against cyber threats.
These forward-thinking organizations of AI have improved network security by overseeing a substantial portion of network communications, approximately 95%, and a significant 90% of endpoint devices, actively seeking out signs of malicious activities and vulnerabilities.
Is AI and Automation Effective?
Indeed, AI and automation form a highly synergistic partnership, significantly enhancing operational efficiency and visibility within organizations.
This alliance proves attributes such as precision, swiftness, accuracy, scalability, and streamlined processes by implementing deep reinforcement learning and other analytical techniques, resulting in optimal results.
3 Ways to Use AI for Security Operations
AI can positively revolutionize the field of cybersecurity.
1. Machine Learning for Pattern Recognition
Machine learning, particularly Deep Reinforcement Learning, emerges as an invaluable tool for recognizing patterns, monitoring new assets and services, and enhancing the functionality of AI models.
This approach significantly improves data analysis, scenario modeling, and the proactive anticipation of potential attack vectors.
2. Leveraging Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing techniques prove instrumental in extracting insights from textual data sources, augmenting threat intelligence, and enriching knowledge repositories.
3. Streamlined Automation
Automation streamlines laborious and time-consuming tasks, expediting response times and alleviating the cognitive burden on human analysts.
By harnessing AI-driven insights, automation tools with AI capabilities excel in threat identification by people, devices, or locations, taking precise actions to notify and escalate incidents.
This strategic alignment allows human experts to concentrate their cognitive efforts on resolving intricate, judgment-intensive challenges.
Some of the universal advantages resulting from the fusion of AI and automation are:
● The expedited identification and response to incidents.
● Establishing robust governance and compliance measures within the security domain.
● The reduced analyst fatigue enables speed, error-minimized decision-making.
● Substantial reductions in cybersecurity costs improved efficiency throughout protection, prevention, detection, and response processes.
● Significant cuts in data breach costs, underscoring the efficacy of detection and response protocols.
● An amplification of ROSI by a substantial margin, exceeding 40%.
AI-driven, automated security measures at access points effectively shield against zero-day threats, malware, and vulnerabilities.
AI and automation augment performance across multiple facets, encompassing speed, insights, flexibility, and scalability.
AI seamlessly assimilates and processes data from structured and unstructured sources, both internal and external. This fusion, augmented by threat intelligence and open-source information, helps cybersecurity analysts with a comprehensive situational understanding, expediting the response to and recovery from security incidents.
A team of AI and automation boosts the work environment by allowing analysts to focus on complex, judgment-reliant problems and enhances governance and compliance by enabling more effective and efficient review and remediation procedures.
Automation alleviates the burden of fatigue and vastly improves the speed and accuracy of decision-making, resulting in a marked enhancement in overall cybersecurity efficacy.
Implementing AI and Automation Strategically
In recent years, as the remote workforce and the prevalence of cloud-based applications and servers have increased, the need for comprehensive endpoint and application monitoring has become increasingly vital.
This growth in connectivity has allowed cybercriminals to exploit these services, giving rise to threat vectors.
What was once a landscape primarily dominated by opportunistic phishing attacks has now evolved into well-coordinated ransomware campaigns, wherein businesses are effectively held hostage until they comply with extortion demands.
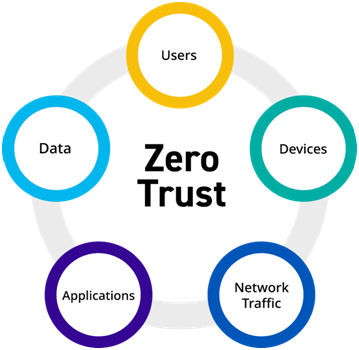
Zero-Trust Model
The most significant business advantage arises when artificial intelligence (AI) is combined with automation within the zero-trust model.
This strategic combination is a strong mechanism for enhancing protection and prevention, effectively catering operational silos, and elevating visibility across an organization's digital landscape.
It also works by encompassing data, devices, users, network infrastructure, workloads, applications, and partner interactions within the ecosystem.
The combined power of AI and automation plays a pivotal role in realizing this comprehensive perspective by conducting regular scans for sensitive data discovery and classification.
This process unfolds not only on-premises but also at the endpoint, during data transit, and within cloud environments. These technologies empower companies to leverage source data and metadata, thus enabling the recreation of the complete context for any digital interaction.
Additionally, they facilitate the identification of the most sensitive data, ignoring who holds access to it and under what conditions, who accesses it and when, and the specific actions taken with it.
This approach not only aids in meeting stringent data privacy and regulatory compliance standards but also increases monitoring and control over access to repositories housing susceptible data.
Human Factor in Technology
Awareness of cyberculture and the presence of skilled cybersecurity professionals play pivotal roles in achieving both security and business objectives.
It is important to note that the success of AI programs does not render human talent obsolete; rather, it augments the efficiency and effectiveness of security analysts and extends the reach of individuals knowledgeable in security matters.
AI introduces a more adaptable engagement model, thereby mitigating some of the challenges associated with resource limitations and skill constraints, positively or negatively influencing the overall security landscape.
By integrating human factors with technological advancements, resource gaps have increased by reinvesting in developing a cybersecurity workforce.
Organizations can nurture talent from within by redefining automation not merely as a cost-saving measure but as a means to foster specialization and improve the work experience, thereby facilitating the expansion of employees' skill sets.
Your Roadmap to AI Automation: Think First!
When you contemplate integrating AI insights and automation into your security operations, it's important to envision what a successful implementation means to your organization.
Learning from experiences
Those who have implemented AI use a combination of ready-made solutions and tools according to their needs.
In cyber risk and compliance, and threat detection and incident response, many organizations find that adaptable. Off-the-shelf software gives the most favorable results.
However, some companies have successfully employed AI custom software. These softwares are developed internally or by a third party. They produce better outcomes when it comes to digital identity and trust management.
What to consider next?
Expense is your most important factor when you consider implementing AI in your organizational system. Your security operations budget is important to manage.
Some AI security applications may also offer advantages in some organizations, like banking and financial markets.
You need to check out:
● Continual support,
● Necessary personnel, and patch management concerning maintenance and addressing vulnerabilities.
Key Points to Consider On Your Way to AI Automation
Evaluate your security performance using key metrics as a reference point. Identify the factors driving security improvements.
Comprehending the compelling reasons behind implementing AI and automation capabilities within your security operations is crucial.
Adjust your cyber risk and cybersecurity strategy to align with these shifting priorities.
This could encompass objectives like diminishing cybersecurity incidents and breaches, achieving cost reductions through operational efficiencies, or enhancing trust among customers, employees, or partners.
Pinpoint areas that warrant enhancement by comparing your metrics to your peers.
Analyze vital risk and security metrics covering protection, prevention, detection, and response, and gauge how your organization stacks up against similar entities.
Highlight zones where you can channel improvement efforts, focusing on areas where the integration of AI and automation can have the most productive impact.
To facilitate security improvement initiatives, ponder on these:
1. Security AI strategy and operational plan
Ensure your AI applications' implementation, governance, technology providers (such as your Internet Service Provider and software compliance), and management align with your broader cyber risk and security strategies. This should show reflection in operational policies, controls, and processes.
2. Identify and cultivate the necessary behavioral and technical skills
Assess how automation may impact your cybersecurity workforce. Is it a threat or an opportunity?
3. Engage in open dialogues to ensure a smooth transition.
When evaluating security AI and automation, consider factors like the work environment, the demand for specialized expertise, and the associated need for upskilling or reskilling.
4. Determine the blend of skills required in an AI-plus-automation environment.
Identify where AI and automation can provide the most significant advantages to your cybersecurity workforce. Identifying the skill gaps and delivering role-specific training to refine the behavioral and technical skills is essential.
Include human factors such as experiential learning and cybersecurity simulations. This polishes skills through practical experiences by utilizing in-house resources(such as reliable VPNs and IP address protection) or external workforce partners.
5. Keep a vigilant eye on your progress
With new AI applications and functionalities, try to validate your actual performance against the benchmarks predefined to match the relative effectiveness of various investments.
Set Priorities as Your Ultimate Goal
Target Impact
Have a look at key performance metrics. Weigh the potential benefits that can be derived from enhancing performance on each of these metrics. Include operational elements such as cost, efficiency, quality, and time.
Security Strategy
Prioritize areas that align with your security strategy and can substantially contribute to your strategic goals. Identify the AI applications that are most likely to enhance performance. Identify the performance metrics closely tied to protection, prevention, detection, and response.
Highlight Strength
Decide on the most suitable AI deployment model, whether it involves configuring an existing solution or a specialized one that complements your strengths, and determine the extent to which you'll rely on third-party support and development.
Will You Adopt AI and Automation as Your Security Partner?
“It’s an AI and automation arms race between cyber defenders and threat actors. They’re using new technologies like generative AI to modernize their tactics and techniques and to adjust procedures in real-time. We need security AI and automation solutions to help us stay a step ahead.” Chief Information Security Officer Consumer goods company.
Artificial intelligence supports the automation process, and its influence on the human element of the equation is even more substantial.
Security analysts continue providing ongoing input to enhance the solution's intelligence while making it more user-friendly.
You might not be a fan of AI models, but you can not deny their positive impacts over the years and the time yet to come.